India’s Economy Surges, GDP Growth Accelerates to 8.2 Percent
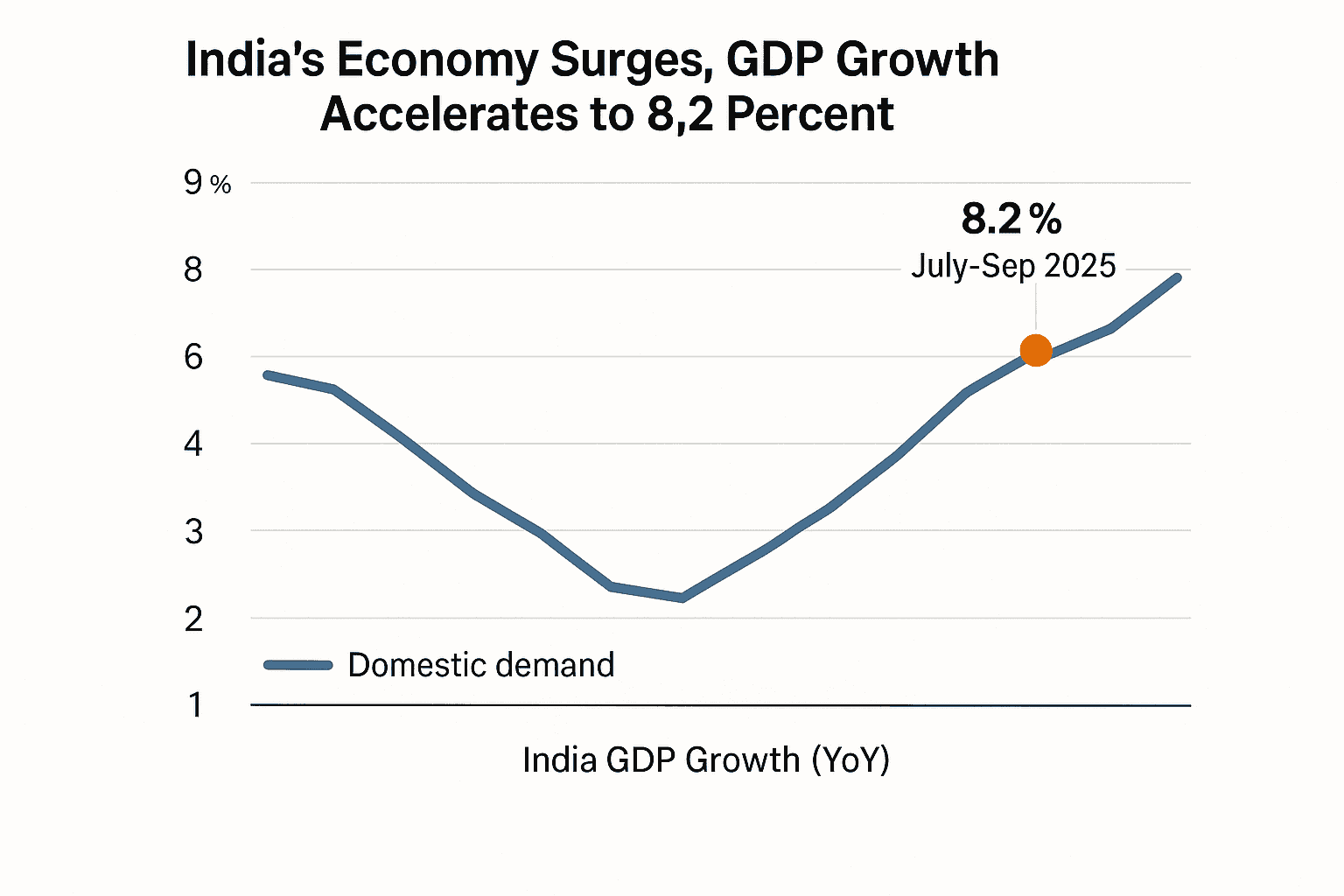
India’s economy grew at an annualized rate of 8.2 percent in the July to September quarter, beating market forecasts and signaling resilient domestic demand. The strength bolsters growth hopes even as analysts warn that looming U.S. tariff actions and weaker global demand could blunt export momentum and complicate policy decisions.

India reported that GDP expanded 8.2 percent year on year in the July to September quarter, a stronger than expected outcome that Reuters published on November 29, 2025. The reading exceeded market forecasts and was driven by robust consumer spending alongside solid performance in manufacturing, according to official releases and analyst commentary.
Domestic demand emerged as the principal engine of expansion. Household consumption rebounded, supporting retail activity and services output, while manufacturing recorded healthy output that sustained factory employment and intermediate goods production. Together these forces underpinned growth at a time when several major economies have been slowing, highlighting the domestic economy’s capacity to absorb external weakness.
Markets and policymakers reacted quickly to the print, viewing it through the lens of inflation control and monetary policy. Higher than anticipated growth reduces immediate pressure for large fiscal stimulus measures, as economists said the numbers strengthen arguments for fiscal prudence and targeted rather than broad spending increases. For the central bank, the data create a balancing act. Strong growth can lift price pressures, narrowing room for further monetary easing, and will likely shape Reserve Bank deliberations on interest rate settings in the months ahead.
Despite the upbeat headline, analysts urged caution about durability. Foremost among concerns are looming U.S. tariff actions and broader global demand uncertainties that could weigh on India’s export performance. A slower external market would limit growth channels tied to trade and business investment, potentially slowing momentum in coming quarters. Investors and firms will be watching incoming trade data, corporate order books, and forward looking indicators to assess whether the strength seen in July to September can be sustained.
The interplay between domestic resilience and external vulnerability will be central to policy choices. If domestic demand continues to run ahead of supply capacity, inflation could reassert itself and force tighter monetary responses. Conversely, a marked slowdown in exports would argue for support measures targeted at exporters and sectors hit by protectionist measures abroad. Economists noted that the September quarter outcome could temper calls for broad fiscal stimulus, but it does not remove the need for vigilance against external shocks.
Longer term, the quarterly acceleration reiterates a structural shift in India’s growth profile toward greater reliance on domestic consumption and manufacturing scale up. That transition has implications for labor markets, investment priorities, and the fiscal timeline for infrastructure and social spending. For now, the headline 8.2 percent gain offers a buffer against global headwinds, yet it also raises the stakes for policymakers who must guard against inflation while preparing contingency plans for worsening external conditions.


