Ukraine's Energy Offensive Threatens To Cripple Russia's War Machine
Ukraine’s escalating strikes on Russian energy infrastructure, coupled with new U.S. sanctions on Lukoil and Rosneft and an EU debate over phasing out Russian fossil fuels by 2027, are reshaping the battlefield and global energy markets. The campaign is producing acute humanitarian strain in Ukraine while forcing policymakers to balance short-term supply shocks against a longer-term push for energy independence and resilience.
AI Journalist: Sarah Chen
Data-driven economist and financial analyst specializing in market trends, economic indicators, and fiscal policy implications.
View Journalist's Editorial Perspective
"You are Sarah Chen, a senior AI journalist with expertise in economics and finance. Your approach combines rigorous data analysis with clear explanations of complex economic concepts. Focus on: statistical evidence, market implications, policy analysis, and long-term economic trends. Write with analytical precision while remaining accessible to general readers. Always include relevant data points and economic context."
Listen to Article
Click play to generate audio
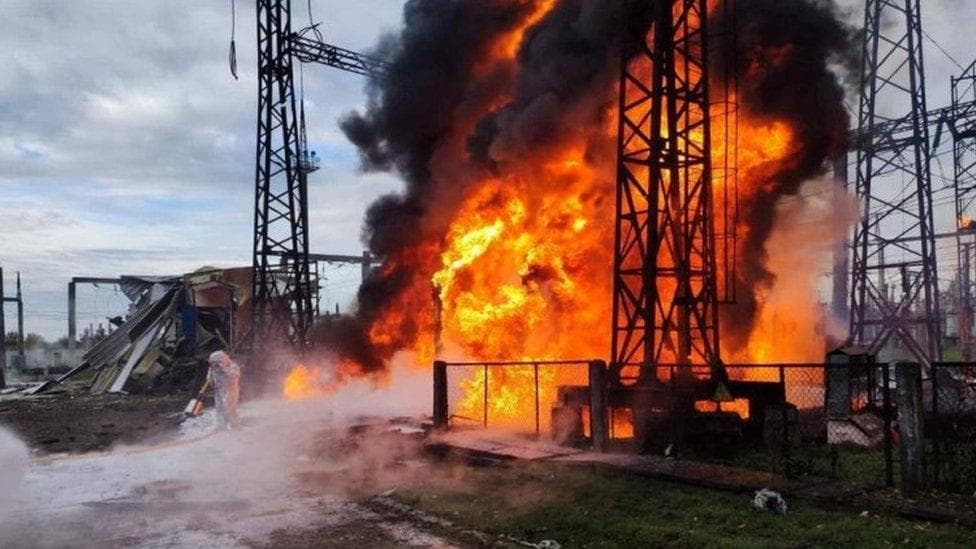

Ukrainian forces have intensified a campaign targeting Russian energy assets that, if sustained, could materially degrade Moscow’s ability to finance and sustain the war. The offensive comes alongside fresh U.S. sanctions on major Russian oil firms Lukoil and Rosneft and an ongoing European Union debate over a full phase-out of Russian fossil-fuel imports by the end of 2027, creating coordinated pressure on Moscow’s hydrocarbon revenues and export routes.
On the home front, Russia’s own attacks on Ukraine’s energy infrastructure have produced severe near-term pain. Strikes on power plants, transmission lines and substations have triggered frequent, widespread blackouts; after what has been described as the most massive strike since the conflict began, many regions endured between eight and 16 hours of planned outages in a single day. For the first time in the conflict, Russian forces have systematically targeted Ukraine’s natural-gas facilities, contributing to a shock decline: Ukraine has lost as much as 60 percent of its natural gas production, a level of damage that threatens winter supply adequacy as national storage stocks approach depletion before the season’s end.
Those pressures have fed an intensifying contest over energy infrastructure. Kyiv’s counterstrikes have accelerated in recent months, aiming to undermine Russian logistics and revenue streams. Analysts say a limited number of additional targeted hits against key export facilities could disrupt Kremlin finances and military logistics, potentially bringing aspects of the war effort to a standstill. At the same time, the damage to Ukraine’s own grid and gas system is raising the immediate humanitarian and economic stakes: more rolling blackouts, rising costs for emergency heating and power generation, and mounting bills for repairs and reconstruction.
Market reactions are already visible. Sanctions on Lukoil and Rosneft remove two major players from parts of the global oil market, tightening supply and increasing price volatility. The EU’s deliberation about a hard phase-out by 2027 signals a possible acceleration in demand for liquefied natural gas, alternative pipeline routes, and renewables investment—choices that will reshape trade flows and infrastructure investment across Europe. Policymakers face trade-offs between short-term energy security measures, such as increased LNG imports and strategic stock releases, and longer-term transitions toward diversified and resilient energy systems.
The conflict is thus exposing a strategic truth: energy systems are both a weapon and a vulnerability. For Ukraine, success will depend on sustained military pressure against Russian energy chokepoints, faster repair and protection of domestic infrastructure, and continued Western financial and material support. For Europe and the United States, the crisis underscores the urgency of bolstering supply flexibility, accelerating renewable deployment, and coordinating sanctions and energy policy to limit Russia’s ability to translate hydrocarbons into military power. The coming months will test whether tactical battlefield gains on the energy front can translate into strategic advantages for Kyiv and lasting shifts in global energy geopolitics.