HHS Rescinds Nursing Home Staffing Rule, Critics Warn Risks
The Department of Health and Human Services rescinded a Biden era rule that set minimum staffing requirements for nursing homes, saying the mandate placed disproportionate strain on facilities in rural and tribal communities. Consumer advocates and public health groups say the move threatens resident safety and widens long standing inequities in long term care.

The Department of Health and Human Services announced on December 3, 2025 that it was rescinding a Biden era regulation that had established minimum staffing requirements for nursing homes nationwide. HHS said the rule disproportionately burdened facilities, particularly those in rural and tribal areas, and risked limiting access to care by forcing some homes to reduce admissions or close.
The decision represents a major policy reversal on long term care oversight and immediately reshapes the regulatory landscape for thousands of skilled nursing facilities that serve older adults and people with disabilities. Proponents of the rescission argue that a federally imposed staffing mandate would have been an unfunded requirement that providers could not meet amid persistent workforce shortages.
Consumer advocates and some public health organizations criticized the move, arguing that minimum staffing levels are closely tied to quality of care and resident safety. These groups say the rescission will leave residents vulnerable to inadequate care, increase the risk of preventable harm, and exacerbate disparities for communities that already face limited long term care options.
Industry groups and nursing home operators welcomed the change, saying the mandate was unrealistic given current staffing shortages and that it could have accelerated facility closures, particularly in regions where attracting and retaining health workers has been historically difficult. Operators said they need more flexible tools and increased resources to stabilize workforces rather than prescriptive federal minimums.
The immediate practical effect is to eliminate a uniform federal floor for staff to resident ratios. Regulators, state officials and facility leaders will now navigate how to ensure quality without the baseline requirement that the earlier rule provided. The rescission is likely to prompt legal challenges and legislative responses from both sides of the debate, setting up a period of uncertainty for residents, families and care providers.
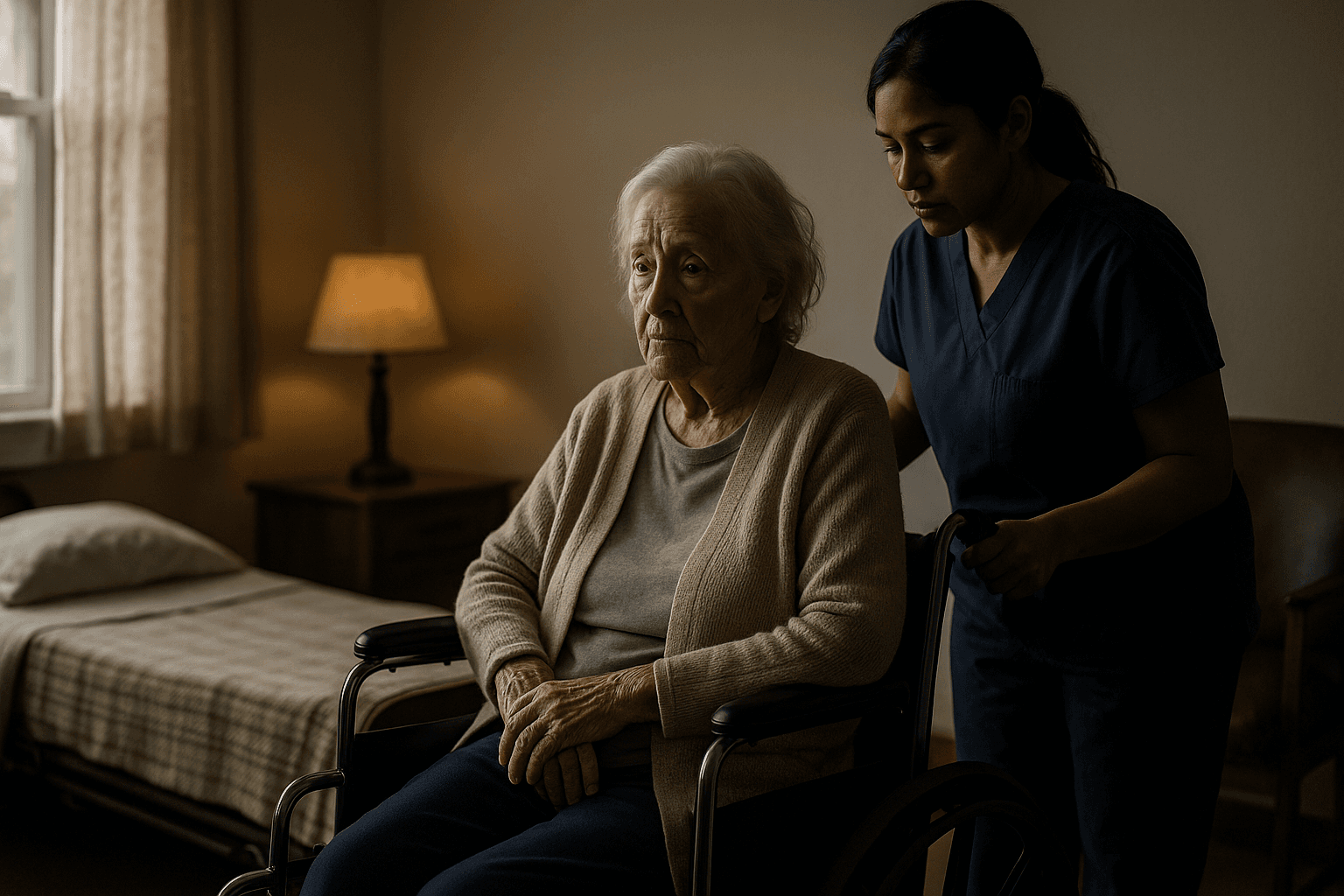
Public health experts warn that any reduction in staffing directly affects the ability of nursing homes to prevent infections, manage chronic conditions and respond to emergencies. Community advocates emphasize that rural and tribal nursing homes, which HHS cited as especially impacted by the rule, already face limited access to clinical resources and often care for higher proportions of residents with complex needs.
Policy analysts say the dispute highlights deeper systemic problems in the long term care sector, including low wages, limited training pipelines, fragmented financing and reliance on Medicaid programs that often pay rates below the cost of care. Without investments to expand the caregiver workforce and reform payment structures, officials fear that regulatory changes alone will not improve outcomes for residents.
Families and resident advocates expressed immediate concern about the implications for everyday care. With legal and legislative pushback expected, the debate over federal authority, resource allocation and how best to secure safe, equitable care for a growing population of older adults is likely to intensify in the months ahead.


