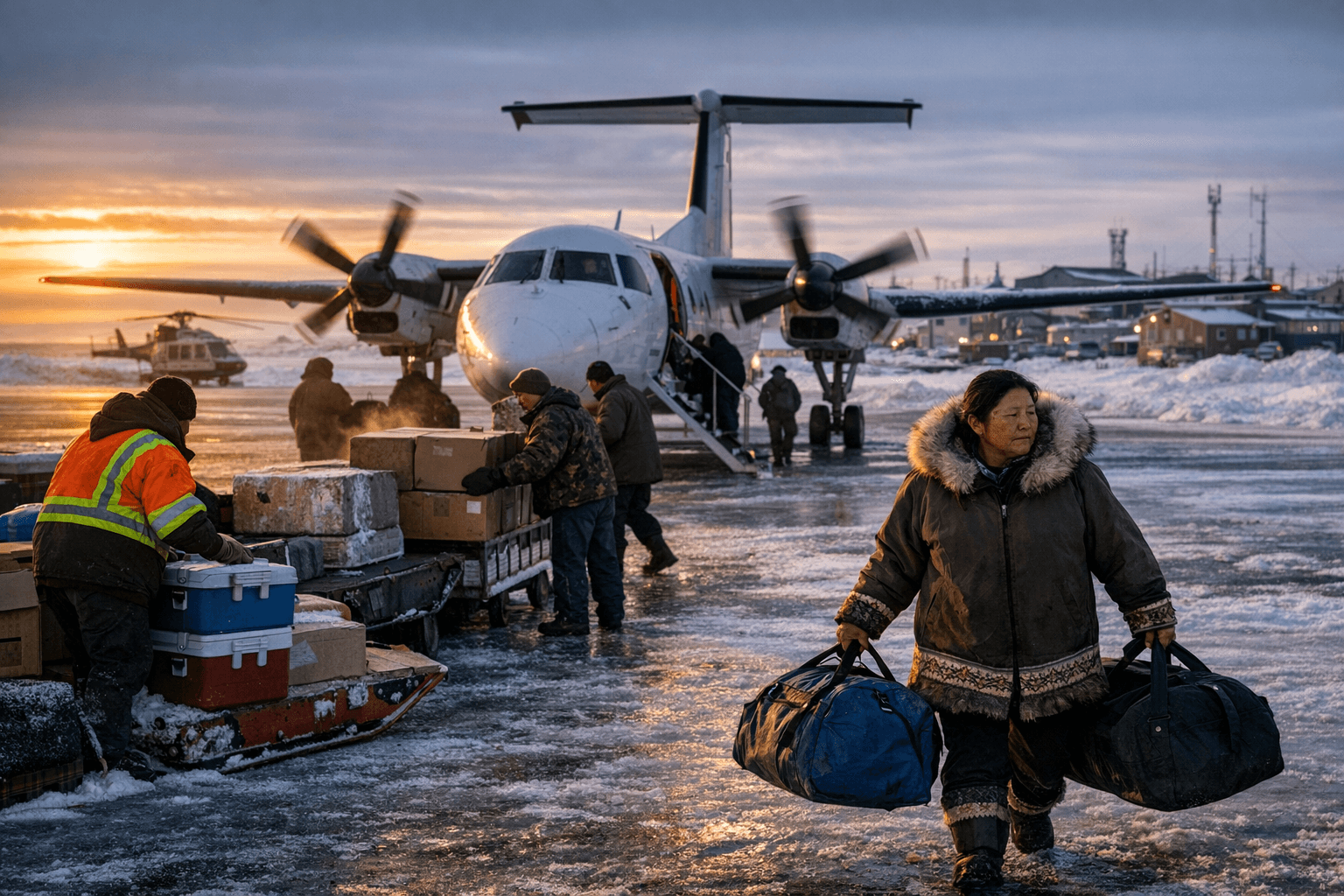Nuiqsut Profile: Remote Inupiat Village Balances Subsistence and Services
Nuiqsut is a small Inupiat village of roughly 400 people located near the Colville River headwaters and the Beaufort Sea, founded in the 1970s by families from Utqiagvik. Its traditional subsistence economy, local institutions and alcohol prohibition shape daily life and create distinct policy and economic priorities for residents and regional officials.
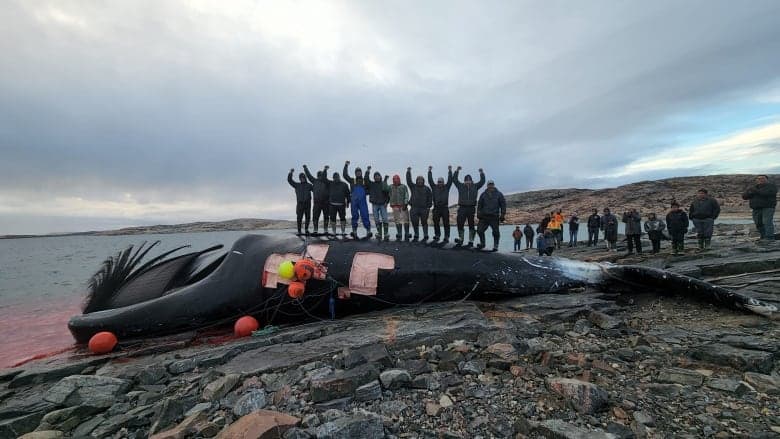

Nuiqsut sits about 135 miles southeast of Utqiagvik on the North Slope, where access, climate and cultural practices define community life. Established in the 1970s by families relocating from Utqiagvik, the village has an estimated population of roughly 400 and remains anchored in a subsistence economy that centers on bowhead whale hunts, caribou harvests, seal hunting and fishing. These activities supply food, social structure and cultural continuity for residents.
Local institutions serve daily needs in a compact community. Trapper School provides primary education, a health clinic delivers medical services, and a public safety building supports local emergency response. Alcohol is prohibited in the village, a policy that has been part of local governance and social regulation. Nuiqsut’s incorporation and its institutional base reflect decades of local organization to maintain services and cultural traditions in a remote setting.
The community’s remoteness and reliance on subsistence activity create clear economic realities. A largely noncash subsistence economy reduces dependence on outside markets for some food needs but increases vulnerability to disruptions in supplies, transportation and environmental change. Costs for fuel, food and building materials remain high across the Arctic, placing pressure on household budgets and on municipal budgeting for infrastructure and services. Maintaining schools, health services and public safety in a village of this size requires continued operational funding and logistical support from borough and state partners.
Policy priorities for Nuiqsut center on supporting subsistence livelihoods while strengthening essential services. That includes investments in healthcare capacity, education and emergency services adapted to remote operations, as well as measures to protect hunting and fishing access that sustain cultural life. Long-term trends that affect Nuiqsut include demographic stability at a small population scale, ongoing needs for reliable transportation and supply lines, and environmental changes in the Arctic that can alter sea and river ice conditions critical to hunting and travel.
For residents and officials in the North Slope Borough, Nuiqsut illustrates the tradeoffs facing many Arctic communities: preserving a living cultural economy based on subsistence practices while securing the public services and infrastructure necessary for health, safety and education. Continued coordination among village leaders, regional organizations and government agencies will shape how Nuiqsut adapts to economic pressures and environmental change while maintaining its cultural identity.
Sources:
Know something we missed? Have a correction or additional information?
Submit a Tip
%3Aquality(70)%2Fcloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com%2Fadn%2FF7TKLQBGCZG45OATFMBSQEKIA4.jpg&w=1920&q=75)