Congress debates nearly $1 trillion defense bill, major Ukraine aid
The House is set to vote this week on the 2026 National Defense Authorization Act, a sweeping near $1 trillion package that bundles large Ukraine security funding with domestic pay and family support and contentious social measures. The bill's mix of foreign security commitments, technology controls and limits on transgender participation in military academies raises immediate public health, equity and community consequences.
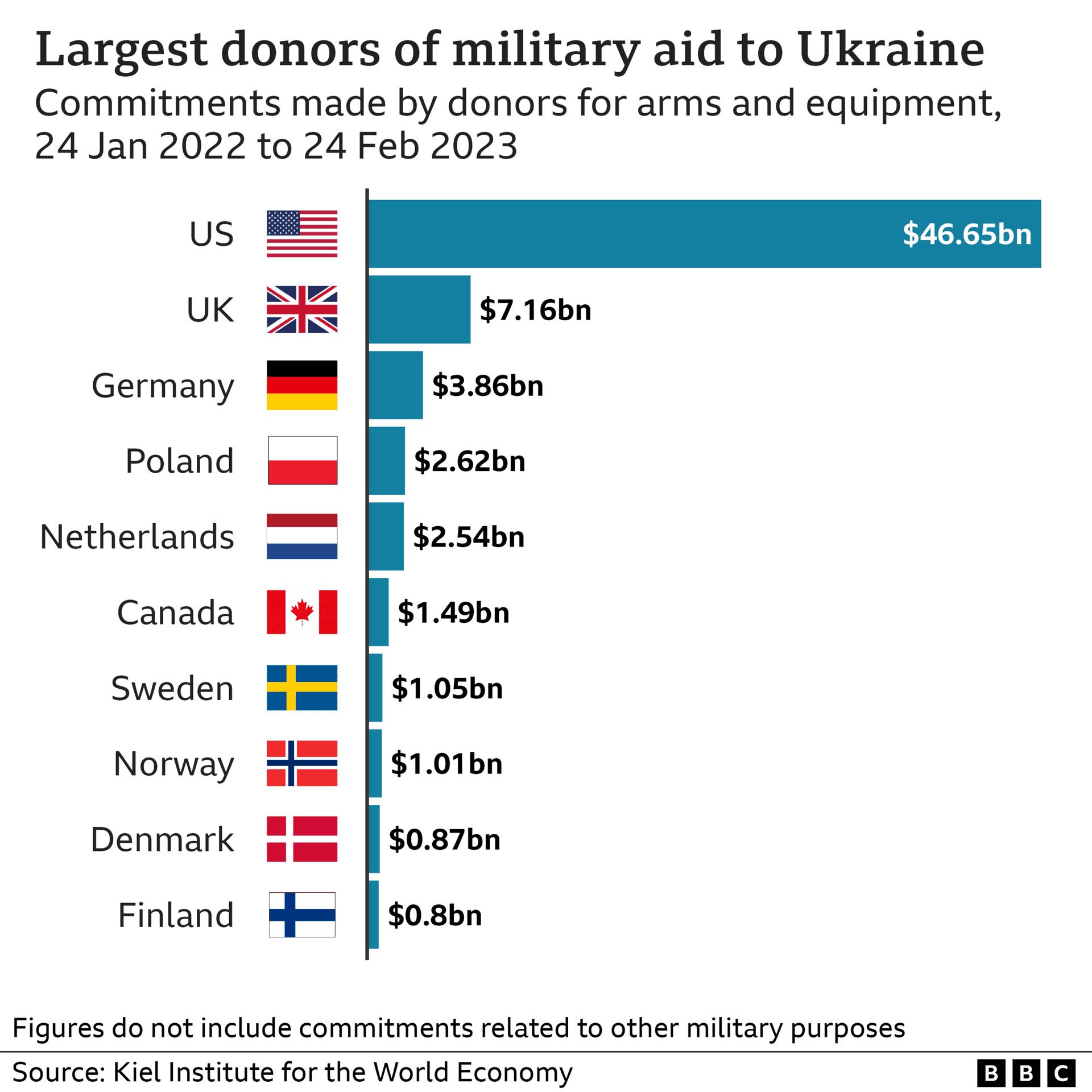
The House is set to vote this week on the 2026 National Defense Authorization Act, a sprawling defense policy bill that combines traditional military priorities with expansive foreign assistance and domestic social policy. The nearly $1 trillion measure includes roughly $400 billion allotted across an initiative for Ukraine security assistance, plus funding and policy steps aimed at strengthening European defenses and supporting Baltic states.
Lawmakers behind the bill framed the package as a response to strategic competition in Europe and Asia. Alongside the Ukraine funding, the legislation authorizes further security assistance to partners in Asia and the Philippines and includes provisions intended to limit reductions in U.S. troop levels in Europe. The scale of the assistance reshapes how Washington directs defense resources, but it also carries public health and humanitarian implications for civilian populations in conflict zones, including displacement, interrupted health services and longer term needs for reconstruction and medical care.
The bill reaches beyond weapons and basing to address economic and technological national security. It would create new screening mechanisms for outbound investment in sensitive Chinese technologies and enact the measure known as the Biosecure Act, which would restrict certain Chinese biotechnology firms from accessing federal funds. Those moves aim to protect supply chains and sensitive research, yet they also risk constraining scientific collaboration and the flow of medical and health technology that global health systems rely on. Public health researchers and community advocates warn that tighter restrictions, if applied without clear safeguards, could slow biomedical innovation and exacerbate inequities in access to vaccines and therapies that depend on international partnerships.
Domestic provisions in the NDAA seek to improve conditions for service members and their families. The bill includes a 4 percent pay raise for troops, expanded childcare and housing measures, all intended to bolster retention and family stability. Those changes have potential downstream effects on community health, especially mental health and economic security among military families who contend with frequent relocations and housing shortages.
At the same time, the legislation incorporates conservative social policy language, including limits on transgender women participating in women’s athletic programs at U.S. military academies. Civil rights advocates and health professionals emphasize that such measures carry real consequences for the mental and physical well being of transgender service members and cadets, and for the culture of inclusivity in military training institutions. Critics argue that policy makers are using the defense bill as a vessel to advance broader cultural priorities that intersect with health care access and civil liberties.
The 2026 NDAA underscores a growing trend in Washington where defense authorization has become a wide vehicle for strategic, economic and social policy. As the House moves toward a vote this week, the debate highlights larger questions about how the United States balances support for allies, safeguarding sensitive technology, and protecting the rights and health of service members and communities at home and abroad.


